What is two-factor authentication? You see this term everywhere but still don’t know about it. 2FA or Two-Factor Authentication can also be called Dual Factor Authentication or Two-Step Verification. It is a security process that requires users to verify their identity twice for authorization.
Two-factor authentication is designed to protect users from unauthorized access. Obviously, 2FA is more secure than Single-Factor Authentication (SFA). In SFA, you only need to use one authentication factor, typically a passcode or password. In 2FA, your passcode or password serves as the first authentication step, while the second factor can be a biometric method (such as face unlock or fingerprint) or a security token.

Hackers dislike 2FA because of its additional layer of protection. This means that having 2FA makes your information and online accounts much safer. With 2FA, even if your password is compromised, your security is not at risk because a second authentication factor is required.
In the past, this type of system was not widely used, but recently many companies have been encouraging their users to enable 2FA. Hackers often try to steal password databases to gain access to users’ passcodes and passwords. Let’s learn everything we can about two-factor authentication.
Two-Factor Authentication
There are many ways that can be used as a second way of authentication. Today, many 2FA are based on knowledge methods. Either the inherence factor or possession factor is used in the two-factor authentication.
Here are listed authentication factors adopted for computing.
1. Possession Factor
This factor refers to something that a user already owns. This could be anything like an ID card, cellphone, security card, application, etc. These possession items help to verify his or her identification.
2. Knowledge Factor
This refers to the knowledge a user possesses that proves they know something confidential. This could be a PIN (Personal Identification Number), password, or similar information. It could also be a question whose answer is known only to the user. Typically, when creating an account, you are asked to set answers to a few security questions, so you can provide the correct answers if asked in the future.
3. Biometric Factor
This is also called the inherence factor. It is something that is inherent physically in the user. The most common personal mapped attribute on the human body is the fingerprint. The 2FA could be a fingerprint that needs to be scanned by a fingerprint scanner. Some other useful biometric factors are voice and facial recognition. Some behavioral inherence like speech patterns or keystroke gesture dynamics can also be used. The most common is fingerprint and that is why in many places you see the same factor.
4. Time Factor
This factor lets the authentication happen only at a specific time. If someone tries to log in at a different time the 2FA won’t allow access.
5. Location Factor
This refers to the authentication which is done by recognizing the location of the person who is trying to complete the authentication. This can be useful when you want a particular device to be only able to get through your authentication within a specific region. The source of the internet used by the device helps to know where that device is being operated. This system is called a GPS (Global Positioning System). Not used commonly by users but is something that is useful and secure.
The most common authentication factors are Knowledge, possession, and biometric factors. But other few are used when the security needs are too high. Some high-security systems even use multi-factor authentication where more than two authentication verifications are required. They are more secure and keep hackers at bay.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
The need for 2FA depends on the user and the service provider. The process is quite similar to your normal single-factor authentication. Just a few steps are added for security. Right now, almost all social media accounts recommend users have two-factor authentication. It also helps to recover your account in case of a breach.
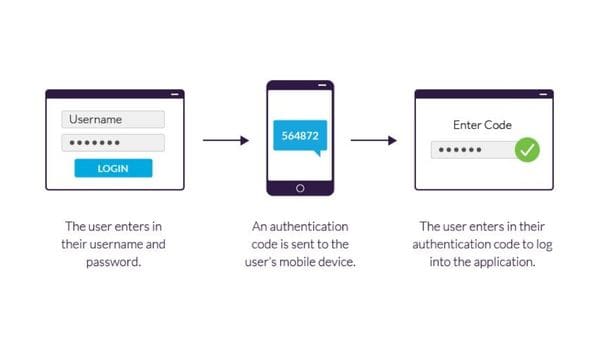
- The user has to log in to a website or app.
- They have to insert their basic information such as a username and a correct password. After this, the particular site analyzes its servers to match the username with the password and lets the user in.
- If your process does not need passwords then the site usually generates a security key that is unique for you. After entering this key the server checks the authentication and verifies you.
- Now, your site will move you to the second stage of login. This step can take a bit more time and can be offered in multiple ways. Here, you will have to provide something that is only limited to you. It could be a security code, biometric, smartphone, ID card, etc. This comes under the possession or inherence factor.
- In the next step, you might receive an OTP (One Time Password). Enter this code to complete the stage.
- After successfully completing both factors, you will get access to operate or use the site of the application.
There is nothing too complicated in this if you have used 2FA. If you remember, you usually have to go through such steps while accessing your online bank application or bank account.
Two-Factor Authentication Elements
If we see two-factor authentication can also be multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA is using two or more authentication methods. So, when the service or system asks you for two authentications it can also come under MFA. But sometimes two factors can not be called 2FA. For instance, giving your password and secret answers comes under single-factor authentication. Because both password and secret answer come under the knowledge factor of authentication.
Talking about single-factor authentication, your password and username are not at all secure. The biggest problem with password authentication is that for a strong and long password, you will need diligence and knowledge.
Why Passwords are not considered strong? Because there are many threats that stand against them such as lying around sticky notes with some old HHDs, etc. Also, some external threats such as hackers and cyber attackers can easily break through your password.
With some time and hard work, a hacker can easily break through a password authentication factor to steal anything they want. Password authentication is still considered Single-factor authentication because of the low protection wall and easy-to-make systems.
Multiple questions for challenging authentication can create a much thicker wall of security. But it also depends on how you have implemented that. In SFA fingerprint, verification can be one of the strong types of factors. Easy and quick to use while being a better choice for safety.
Types Of Two-Factor Authentication Products
Some various services and devices implement the 2FA. This can vary from radio frequency to tokens. These products can easily be divided into two categories.
- Software or infrastructure that authenticates or recognizes access of users who are trying to use their token correctly.
- The token is given to you while logging in.
These tokens are usually physical types of items like smart cards or key fobs or even be in your smartphone or smartwatch. Having a PIN code generator in your PC software can also be called a token product. The PIN code generator is commonly known as OTP (One Time Password). Generally, they are created by a server and then verified by software or applications. OTP is temporary and links to your particular device or account. As the name suggests they are only used once.
The company or organization has to create a system that can process, accept, and then allow or deny the specific authentication token. This system could be a hardware, software, or third-party type of vendor.
Another concept that 2FA follows is allowing the user to access only what they have verified themselves for. This means one key of 2FA is always linked to the authentication system. This system is connected to the organization’s authentication data. For instance, Microsoft provides the necessary infrastructure to support 2FA in Windows 10 through Windows Hello. This system authenticates your Microsoft account while verifying your identity.
Smartphones Two Factor Authentication
Your phone offers various capabilities for 2FA, allowing companies to build their systems more efficiently. Almost all smartphones today are equipped with a fingerprint sensor, front camera (for facial recognition or eye scan), and a microphone (for speech recognition). The built-in smartphone GPS is used for location-based authentication. For out-of-band authentication, voice calls or SMS are used.
Your mobile number can provide a verification code or OTP through a phone call or SMS. For smartphone-based 2FA, you will need to verify using a single phone number.
Push Notification’s Two-factor Authentication
In this method, no password is used for authentication. Instead, user verification is done by sending a simple notification to a secured application on your device. This alerts you (the user) so you know someone has attempted to authenticate. The push notification typically shows basic details and provides two options: Accept or Deny. This process can be completed with just a few clicks. If you accept, the system or authenticator will grant access. Denying it will secure your account or authentication within seconds.
Push notifications are only sent to devices registered within the system. The most common device for receiving these notifications is a mobile phone. However, if your device is compromised, your notifications could also be at risk. Push notifications help mitigate risks such as man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized social engineering access.
Is 2FA Secured?
Yes, 2FA does enhance your overall security, but some 2FA schemes can make your system weaker. For example, hardware tokens are completely dependent on the security of the manufacturer or issuer. A notable incident related to this was the compromise of RSA Security’s 2FA in 2011. According to the company, their authentication system, SecureID, was hacked.
The hackers easily gained access to the company’s chief executive’s email to infiltrate their system. This does not mean that 2FA is bad or useless. It simply means that, while 2FA is stronger than SFA, it can still be breached. Ideally, a company should implement more layers of authentication, but for regular users, 2FA is generally sufficient.
Final Words
There are many more places where 2FA can be applied and used. The future of two-factor authentication is solid and it will definitely help our security. Smartphone companies will keep working on their technology to provide much better compatibility. It is not a complex topic to understand but still, people don’t take it seriously.
If you don’t have 2FA on your social media accounts or on other services it is time you give it a try. There are many stories where this authentication failed but there are many more where it succeeded in protecting the users. What are your thoughts on two-factor authentication?